Radiographically the accessory tissue resembled the remaining normal glandular tissue but was separate from it. Overall 94 of ectopic breast tumours occur in aberrant tissue and only 6 in accessory breasts.

Sonographic Findings Of Accessory Breast Tissue In Axilla And Related Diseases Lim 2017 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library
It is found anywhere along the milk lines with axillary localization being most frequently reported AB is thought to be an embryonic mammary tissue remnant that can occur with or without the nipple and areola 23It is associated with an incidence of 16 in.

. They are very rarely seen in the face back and thigh. Accessory breast tissue may occur outside milk line at neck face arms hips and back5 The incidence of accessory breast tissue within milk line is 60 to 70 out of these 20 are seen as accessory breast in axilla6 The accessory breast tissue is. Accessory axillary breast tissue is due to residual breast tissue that remains after normal embryologic development.
Axillary breast tissue affects between 2 and 6 percent of women. Both benign and malignant diseases that occur in the normal breast can also develop in accessory breast tissue in the axilla. Common in sternum region.
It is not connected to the pectoral breast tissue. The mean radiographic dimension of the accessory tissue which was best. 4 9 10 and can be appreciated on mammography ultrasound and MRI.
Failure of involution of the milk line results in accessory breast tissue most commonly in the axilla but it can occur anywhere from the axilla to the inguinal region. Accessory breast tissue itself is normal and should not be misdiagnosed as an abnormality. Accessory axillary breast tissue is an uncommon condition.
At the site of pain and swelling pointed by the patient in the right axilla there is the heterogeneous hyperechoic area below the skin. Check out my new series below. 1 The variability of presentation and the possibility of other disease make this problem clinically challenging and although it is a well-known entity there is no established classification system to guide its management.
2 Determining which surgical technique to use is critical to achieving an optimal. The pathology literature reports that it can sometimes be difficult to differentiate breast carcinoma in axillary accessory breast tissue. Radiographically the accessory tissue resembled the remaining normal glandular tissue but was separate from it.
WHY IT MATTERS. It frequently presents as a palpable axillary lump. Sonographic Findings of Accessory Breast Tissue in Axilla and Related Diseases.
The axillary artery is patent. Mammographic features of normal accessory axillary breast tissue were analyzed in 13 women 54 of whom had positive findings on physical examination. Accessory breast tissue itself is normal and should not be misdiagnosed as an abnormality.
We report a galactocele with malignant appearance on ultrasound in the accessory breast. It shows the same appearance as that of the normal glandular tissue of the breast. Fibroductal tissue and lobules of fat are visualized.
Both benign and malignant diseases that occur in the normal breast can also develop in accessory breast tissue in the axilla. The mean radiographic dimension of the accessory tissue which was best seen on oblique or. Radiologists should be able to recognize the imaging appearance of this normal variant on mammography and ultrasound.
The patient was a 32-year-old lactating woman presented to our hospital for considerable swelling in the left axilla. Accessory breast tissue also known as polymastia is a relatively common congenital condition in which abnormal accessory breast tissue is seen in addition to the presence of normal breast tissueThis normal variant can present as a mass anywhere along the course of the embryologic mammary streak axilla to the inguinal region. Accessory breast tissue occurs in 26 of women Fig.
Accessory breasts consist of ectopic breast tissue that results from a failure of the embryonic mammary ridge to regress. Accessory breast tissue results from failed regression of primitive mammary tissue and is most often located in the axilla. Ultrasound of the breast with axilla and mammography revealed features of malignant lesion in the right accessory breast.
35 We report a case of carcinoma of accessory breast. Mammographic features of normal accessory axillary breast tissue were analyzed in 13 women 54 of whom had positive findings on physical examination. When accessory tissue occurs both benign and.
A specific radiography-aided diagnosis of accessory axillary breast tissue can eliminate unnecessary biopsy. At least 6 of the population has accessory breast tissue in their axilla. There is no solid or cystic mass lesion in it.
Ultrasound examination revealed a. The appearance of accessory breast tissue on ultrasound irrespective of location is the same as the appearance of breast tissue within the breast. Accessory breast tissue results from failed regression of primitive mammary tissue and is most often located in the axilla.
The ultrasound shows accessory breast tissue in the axillary without any associated pathology. Accessory breast AB is defined as the presence of extra and ectopic breast tissue. Accessory breast tissue can be found anywhere along the thoracoabdominal region of the milk line the embryologic mammary streak but are most frequently found in the axilla and may occur bilaterally.
Unlike CT and MRI in cases of lymphadenopathy ultrasound can evaluate important parameters such as shape marg. They are most common in the anterior axillary line 12 and are subject to the same disease processes as normal breast tissue. Galactoceles are the most common benign breast lesions during breastfeeding period that can mimic carcinomas.
The ultrasound shows accessory breast tissue in the axillary without any associated pathology. Epub 2017 Apr 3. Any pathologic process that occurs in the breast can also occur in the accessory tissue.
A female presented with a history of the right axillary region pain and swelling during a premenstrual time. Which revealed poorly differentiated carcinoma of the breast. They occur in 046 per cent of the general population but are more common in Asian women 3.
Accessory breasts are classically distributed along the embryonic milk line and are. In recent years many affected women have had a plastic surgery. A Axillary ultrasound shows multiple hypoechoic lymph nodes long thin arrows.
When found on mammography accessory axillary breast tissue should be recognized as a normal developmental variant rather than considered a pathologic lesion although carcinoma can develop in the accessory tissue. Accessory axillary breast tissue is located in the axilla armpits where it can cause diagnostic difficulty especially if it is large. Breast Ultrasound Accessory Breast Tissue vs Axillary Tail of SpenceLooking for a specific breast pathology on ultrasound.
Accessory breast tissue derives from a failure of the primitive mammary tissue to regress after development of the mammary ridge in the thoracic area at week 7 of gestation.

Accessory Breast Tissue Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Sonographic Findings Of Accessory Breast Tissue In Axilla And Related Diseases Lim 2017 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library

Ultrasound Scan Of Right Axillary Accessory Breast Tissue Shows Focal Download Scientific Diagram

Accessory Breast Tissue Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Accessory Axillary Breast Tissue
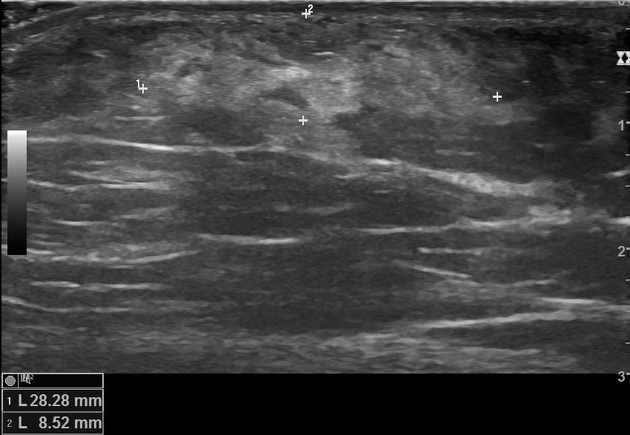
Accessory Breast Tissue Axilla Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Sonographic Findings Of Accessory Breast Tissue In Axilla And Related Diseases Lim 2017 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library

Sonographic Findings Of Accessory Breast Tissue In Axilla And Related Diseases Lim 2017 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library
0 comments
Post a Comment